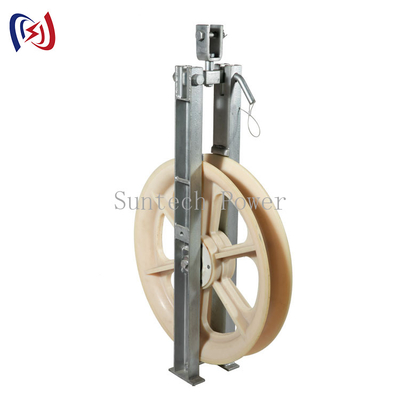
Stringing blocks are essential tools in the power transmission and telecommunication industries, used to guide and protect cables or conductors during installation. Whether you're working on overhead power lines, fiber optic cables, or other wire installations, selecting the right stringing block can significantly impact efficiency and safety.
This guide will explore the different types of stringing blocks, their applications, and key factors to consider when purchasing one—helping you make an informed decision based on your project needs.
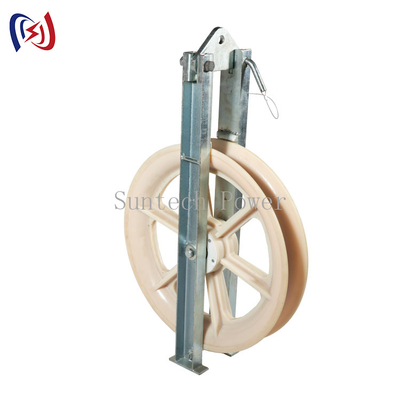
What Is a Stringing Block?
A stringing block is a pulley-like device designed to support and guide cables, wires, or conductors during installation. It minimizes friction, prevents damage to the cable, and ensures smooth operation when pulling lines over long distances or around corners.
Stringing blocks are commonly used in:
- Power line construction and maintenance
- Telecommunication cable installations
- Railway electrification projects
- Renewable energy projects (e.g., wind or solar farms)
Types of Stringing Blocks
Stringing blocks are categorized based on wheel material and number of wheels. Each type has unique advantages suited for different applications.
1. Wheel Material
(1) Nylon Wheel Stringing Blocks
- Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and gentle on cables. Ideal for fiber optic or delicate wire installations.
- Cons: Lower heat resistance compared to metal wheels; not suitable for heavy-duty power lines.
(2) Aluminum Wheel Stringing Blocks
- Pros: Durable, heat-resistant, and suitable for high-tension power lines.
- Cons: Heavier than nylon; may cause abrasion on softer cables if not properly aligned.
(3) Rubber-Coated Aluminum Wheel Stringing Blocks
- Pros: Combines the strength of aluminum with the cable protection of rubber. Reduces conductor damage and noise during operation.
- Cons: Slightly more expensive than standard aluminum wheels.
2. Number of Wheels
Stringing blocks come in single-wheel or multi-wheel configurations (3, 5, or 7 wheels).
- Single-wheel blocks: Best for lightweight cables or short-distance pulls.
- Multi-wheel blocks: Distribute tension evenly, reducing wear on conductors. Ideal for:
- 3-wheel: Medium-duty power lines.
- 5/7-wheel: Heavy-duty installations or bundled conductors.
How to Choose the Right Stringing Block?
When selecting a stringing block, consider the following factors:
1. Cable Type & Weight
- Fiber optic/telecom cables: Nylon or rubber-coated wheels are preferable.
- HV power lines: Aluminum or rubber-coated aluminum wheels handle higher tension.
2. Working Environment
- Coastal/high-humidity areas: Corrosion-resistant materials (nylon or coated aluminum).
- High-temperature zones: Aluminum wheels withstand heat better.
3. Installation Distance & Tension
- Longer pulls or higher tension require multi-wheel blocks to reduce cable stress.
4. Budget & Longevity
- Nylon is cost-effective for light use; aluminum offers long-term durability.
Proper Maintenance Tips
To extend the lifespan of your stringing block:
- Clean wheels regularly to remove debris.
- Lubricate bearings (if applicable).
- Inspect for cracks or wear, especially after heavy use.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 










